A solar all-in-one inverter typically combines the functions of both a charge controller and an inverter, making it a more convenient and space-saving option. However, it may be more expensive. On the other hand, a separate charge controller with an inverter allows for greater flexibility and customization, but it also requires more space.
Let’s explore the features and considerations of both combined systems and separate units of solar charge controller plus inverter in more detail:
Table of Contents
All-in-One Inverter-Charger (Solar Hybrid Inverter)
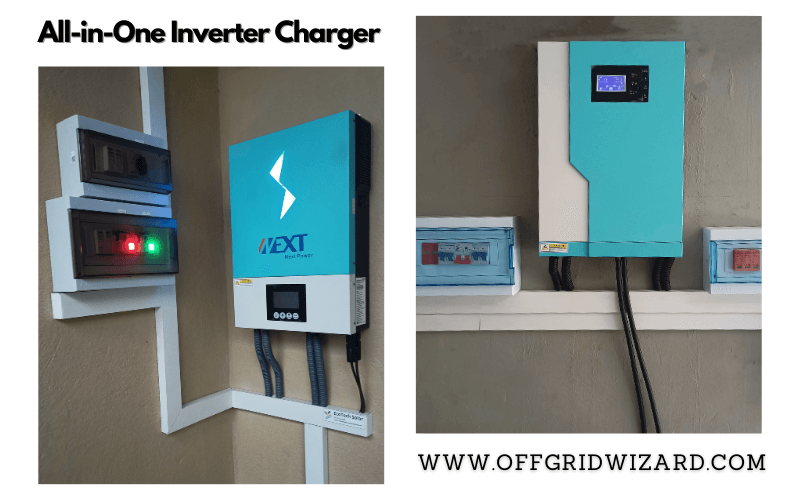
System Integration:
A solar hybrid inverter combines the functions of a charge controller, inverter, and sometimes even a battery management system into a single unit. This integration simplifies the installation process while reducing the overall footprint of the system.
Efficiency & Power Flow Management:
Solar hybrid inverters are designed to maximize the efficiency of the solar power conversion process. They optimize the power flow between the solar panels, batteries, and the electrical grid (if present), ensuring efficient energy utilization. They ensure that energy is efficiently generated, stored, and utilized based on the system’s configuration and user preferences.
Battery compatibility:
Many solar hybrid inverters are compatible with different types of batteries, including lead-acid, lithium-ion, and even advanced energy storage systems like Tesla Powerwall.
Monitoring and control:
Hybrid inverters often come with built-in monitoring and control capabilities. Thus, you can monitor your solar system’s performance, track energy production and consumption, and adjust settings as needed.
Cost:
Solar hybrid inverters tend to be more expensive compared to separate units due to their integrated functionality.
Separate Charge Controller plus Inverter:
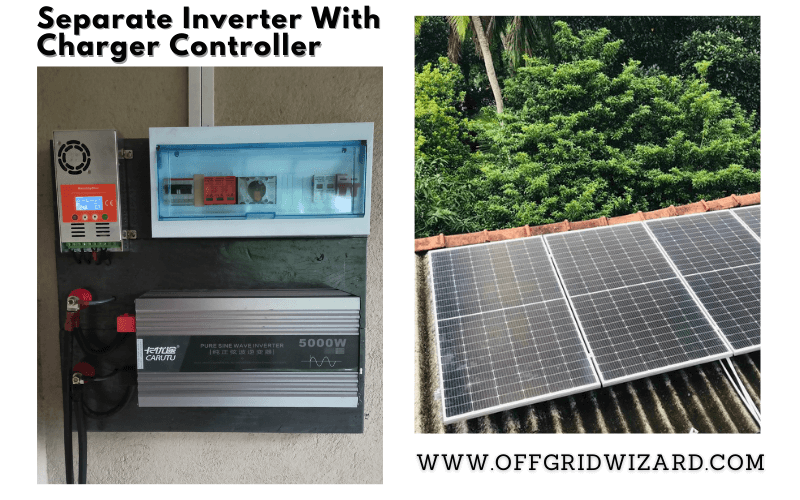
Efficiency & Power Flow Management:
The efficiency of the charge controller can vary depending on the type and quality of the controller chosen. There are two main technologies: MPPT and PWM. MPPT(Maximum Power Point Tracking) charge controllers generally offer higher efficiency compared to PWM (Pulse-Width Modulation) controllers, as they try to track and adjust the voltage and current to extract the maximum power from the solar panels.
Similarly, high-quality inverters typically have high-efficiency ratings, converting the generated DC power from the solar panels into AC power with minimal losses.
In a separate charge controller plus inverter setup, the power flow management between the solar panels, batteries, and the grid may require additional components or manual configuration. If not properly designed or configured, this can impact the overall system efficiency.
Flexibility:
With a charge controller plus inverter setup, you have the flexibility to choose separate components that meet your specific requirements. For example, if you need a high-capacity battery bank for extended power storage and a high-efficiency MPPT charge controller to maximize solar energy harvest, you can select each component based on its performance and compatibility with your system. However, it requires careful selection and configuration to ensure optimal efficiency and performance.
Scalability:
If you plan to expand your solar system in the future, separating the charge controller and inverter allows for easier system upgrades. You can add more solar panels or batteries without needing to replace the entire unit.
Customization:
When using separate components, you have more control over the features and specifications of each device. This can be advantageous if you have unique requirements or want to optimize your system for specific purposes.
Cost:
A charge controller plus inverter setup involves purchasing separate units, which may offer more flexibility in terms of cost. You can choose components based on your budget and specific requirements. However, it’s important to consider any additional components or accessories you might need, such as wiring and monitoring devices.
Which one is Better?
It’s worth noting that the efficiency and performance of both options can vary depending on the brand, model, and quality of the equipment chosen. When comparing different products, it’s advisable to review the specifications and efficiency ratings provided by the manufacturers to make an informed decision.
Consider the physical space available for installation. If space is limited, a solar hybrid inverter can be a more compact option, as it integrates multiple functions into a single unit. A charge controller plus inverter setup requires separate devices, which may require more space for installation.
Consider your future plans for system expansion. If you anticipate adding more solar panels or batteries in the future, a charge controller plus inverter setup allows for easier scalability. You can upgrade individual components without replacing the entire system. On the other hand, a combined unit may be more difficult to upgrade or expand.
The cost difference may vary depending on the size of your solar system. For smaller systems, the cost difference may be less significant, while larger systems may see a more noticeable price gap. It’s recommended to evaluate the specific components, brands, and features you require for your solar system and compare prices from different manufacturers and suppliers to determine the most cost-effective option for your needs and budget.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the choice between a solar hybrid inverter and a charge controller plus inverter depends on your priorities, system size, budget, and future plans. If you prioritize convenience, space-saving, and integration, an all-in-one unit may be the better option. If you value flexibility, customization, and cost-effectiveness, a charge controller plus inverter setup might be more suitable. Read our Complete guide to solar off-grid systems to start your off-grid journey.